This article explains which clinical tools are available in Bp Omni, and how to use them.
Clinical tools can assist with the diagnosis and management of patient conditions.
Bp Omni offers the following clinical tools:
- Disability of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand Score (DASH11)
- Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21)
- Global Rating of Change Scale (GRCS)
- K10
- Numeric pain rating scale (NPRS)
- Örebro Musculoskeletal Pain Screening Questionnaire
- Patient Specific Function Scale (PSFS)
- RAND-36
- Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS)
Disability of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand Score (DASH11)
- From the patient/client tree in the clinical record, go to Clinical tools > DASH11. The DASH (Disability of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand) Score screen will appear.
- Record the Patient or Client's answers to the questions.
- Click + Add work module or + Add sports/performing arts module to add further context specific questions.
- Click Save or Save & close. A summary of the results will appear.


Any previous DASH11 results will display in the Clinical tools panel.
The following provides more information about the calculation logic used by this clinical tool, which may assist in assessing suitability for use at your practice.
Description: The DASH11 is designed to measure symptoms in people with musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limb.
Source: The DASH11 was developed by the Institute for Work and Health, Toronto Canada.
Calculation: See the QuickDASH scoring instructions.
Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21)
- From the patient/client tree in the clinical record, go to Clinical tools > DASS-21. The Depression, Anxiety & Stress Scale 21 (DASS-21) screen will appear.
- Record the patients' responses to the questions.
- Click Save or Save & close.

A summary of the results will appear and structured notes will be generated in Today's notes.

The following provides more information about the calculation logic used by this clinical tool, which may assist in assessing suitability for use at your practice.
Description: The Depression Anxiety Stress Scale has been shown to be a valid and reliable measure of the dimension of depression, anxiety, stress and general psychological distress. The form has 21 items and are each rated on a 4-point scale of how much each particular statement applies to the person. DASS-21 is a self-report instrument.
Source: Lovibond SH, & Lovibond PF. (1995). Manual for the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (2nd. ed). Sydney, Australia: Psychology Foundation.
Global Rating of Change Scale (GRCS)
- From the patient/client tree in the clinical record, go to Clinical tools > GRCS. The Global Rating of Change Scale screen will appear.
- Enter a Diagnosis, and indicate of it relates to the patients left or right side, or neither.
- On the scale provided, indicate the Patient or Client's answer to the question 'How do you describe yourself now compared to when you first came in for treatment?'.
- Click Save or Save & close. A summary of the results will appear.
- Any previous GRCS results will display in the Clinical tools panel.

The following provides more information about the calculation logic used by this clinical tool, which may assist in assessing suitability for use at your practice.
Description: The GRCS provides a means of measuring self-perceived change in health status with the main purpose to quantify the extent to which a patient has improved or deteriorated over time.
K10
- From the patient/client tree in the clinical record, go to Clinical tools > K10. The K10 screen will appear.
- Record the patients' responses to the questions.
- Click Save or Save & close. A summary of the results will display.

The following provides more information about the calculation logic used by this clinical tool, which may assist in assessing suitability for use at your practice.
Description: The Kessler Psychological Distress test (K10) measures a patient's psychological distress.
Source: The Kessler Psychological Distress test (K10) was developed in 1992 by Professors Kessler and Mroczek.
Calculation: The Kessler Psychological Distress test is a 10 item questionnaire. The questions are answered using a five-point scale, where 5 equates to 'all the time' and 1 equates to 'none of the time'. The patient is asked to select the answers which best represent how they have felt over the past four weeks. A higher score indicates a higher level of distress.
Numeric pain rating scale (NPRS)
- From the patient/client tree in the clinical record, go to Clinical tools > NPRS. The Numeric Pain Rating Scale screen will appear.
- Indicate the patient's pain levels as per the instructions on screen.
- Click Save or Save & close. A summary of the results will display.

The following provides more information about the calculation logic used by this clinical tool, which may assist in assessing suitability for use at your practice.
Description: Use the NPRS to record the Patient or Client's perceived pain level.
Source: McCaffery, M., Beebe, A., et al. (1989). Pain: Clinical manual for nursing practice, Mosby St. Louis, MO
Calculation: Items are scored on a scale on 0 - 10, with 0 indicating the lowest level of pain and 10 representing the highest level of pain. The score provided is the sum of the scores divided by the number of activities.
Örebro Musculoskeletal Pain Screening Questionnaire
- From the patient/client tree in the clinical record, go to Clinical tools > ÖREBRO. The Örebro Musculoskeletal Pain Screening Questionnaire screen will appear.
- Record the patients' responses to the questions.
- Click Save or Save & close. A summary of the results will display.

The following provides more information about the calculation logic used by this clinical tool, which may assist in assessing suitability for use at your practice.
Description: The Örebro Musculoskeletal Pain Screening Questionnaire is designed to predict long term disability and failure to return to work.
Source: The Örebro Musculoskeletal Pain Screening Questionnaire was developed by Professor Steven J. Linton at Örebro University.
Calculation: Items are scored on a scale of 1 - 10, with a higher score indicating higher risk of failure to return to work.
Patient Specific Function Scale (PSFS)
- From the patient/client tree in the clinical record, go to Clinical tools > PSFS. The Patient Specific Function Scale screen will appear.
- Enter a Condition, and indicate of it relates to the patients left or right side, or neither.
- Fill out the Activities section as per the instructions on screen.
- Click Save or Save & close. A summary of the results will display.

The following provides more information about the calculation logic used by this clinical tool, which may assist in assessing suitability for use at your practice.
Description: Use the PSFS to quantify activity limitation and measure functional outcome for patients with an orthopaedic diagnosis.
Source: PSFS developed by: Stratford, P., Gill, C., Westaway, M., & Binkley, J. (1995)
Calculation: Items are scored on a scale on 0 - 10, with 0 indicating the lowest level of ability and 10 representing the highest level of ability. The score provided is the sum of the activity scores divided by the number of activities.
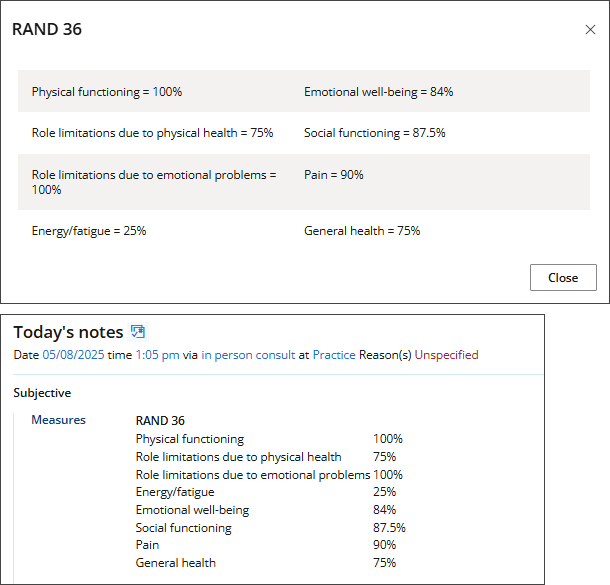
RAND-36
- From the patient/client tree in the clinical record, go to Clinical Tools > RAND36. The RAND-36 screen will appear.
- For each question in the survey, select the option that most closely represents your patient's answer.
- There are 36 optional questions on the survey. After answering the first question, you have the option to Save or Save & close.
- Results will display in the Clinical Tools panel and structured notes will be generated.

The following provides more information about the calculation logic used by this clinical tool, which may assist in assessing suitability for use at your practice.
Description: Use the RAND36 tool for a measurement of health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
Source: The 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) was developed by RAND in 1992.
Calculation: The RAND-36 is a profile measure that yields eight scale scores and two summary scores (physical and mental health).
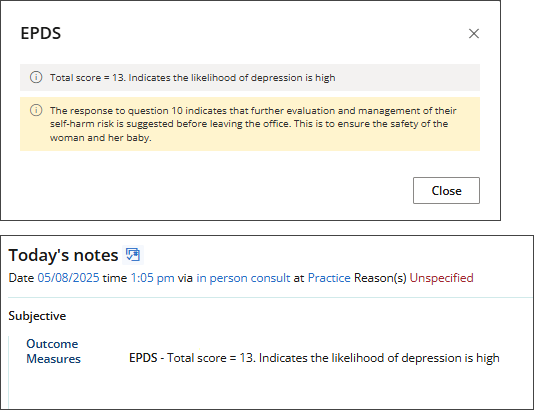
Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS)
- From the patient/client tree in the clinical record, go to Clinical Tools > Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. The EPDS questionnaire screen will appear.
- For each section in the questionnaire, select the option that most closely represents your patient's answer.
- There are 10 sections in the questionnaire. Click Save or Save & close once all questions have been answered.
- Results will display in the Clinical Tools panel and structured notes will be generated.

The following provides more information about the calculation logic used by this clinical tool, which may assist in assessing suitability for use at your practice.
Description: The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) is a self-report scale developed by J. L. Cox and colleagues to screen for postnatal depression. A score above the threshold of 9 or 10 indicates possible depression. Women who score above 12 or 13 are more likely to have depression of various severity.
Source: Cox, J. L., Holden, J. M., and Sagovsky, R. 1987. Detection of postnatal depression: Development of the 10-item Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. British Journal of Psychiatry 150:782-786.
Last updated: 12 August 2025.